Lithium Ion Batteries
A Change
Lead Acid to Lithium Ion
Currently in Indian scenario, most of the applications are designed around lead acid batteries due to its low initial cost, ease of availability and low integration hassles. It has been greatly observed that, this leads to applications often under-performing, causing break-down, and not being able to achieve its full capability. This phenomenon is evident in various applications as back-up supply/ UPS (at all levels: small, medium to large scale), solar power storage, electric vehicles, etc.
In such a changing and demanding situation, where applications are often market driven, the need for a more reliable alternate for energy storage is growing now more than ever before. While choosing an alternative energy storage device, system designers and integrators often find it difficult and often confusing to identify the right energy storage device to fit into their need of application. Some of the alternate energy storage devices include lithium-ion batteries, sodium sulfur batteries, vanadium redox batteries, super-capacitors, etc.
Generally, the broad design considerations are based on the following key requirement parameters:
- Charge time – Time available to charge the batteries
- Discharge requirements/ Rate performance – Greater “C” rates for quick acceleration
- Cycle life – Need for long life
- Operating time – Long life between charges, due to greater depth of discharge
- Operating temperatures – Depending on the application, from -40°C to +65°C
- Weight – effecting mounting and mobility issues.
- Footprint/available space – volume reduction when space matters
- Modularity/Scalability – Ease of system integration, expansion and relocation
- Service/maintenance – projected life for specific operating temperatures and accessibility for servicing and maintenance
- Cost – One of the most important factor, which is often judged by the initial cost alone. However, to arrive at a proper costing of the storage device, the initial cost should be apportioned over the entire operating time (including the maintenance and service costs) has to be considered.
- Lateral integration – Other system changes and maintenance to be made to incorporate the storage device.
Considering the above parameters, the next generation Lithium Ion batteries fit into the alternate choice perfectly.
________________________________________________
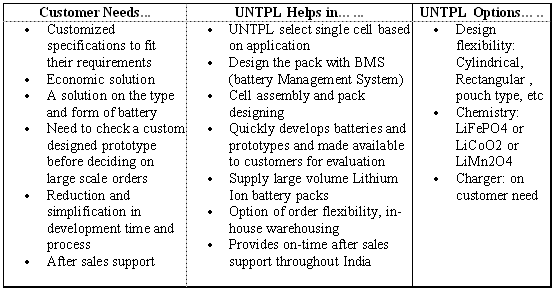
Customers & UNTPL
________________________________________________________________________________
UNTPL firsts
- Bulk Scale Nano Engineered Materials Manufacturer
- Bulk Scale Lithium-ion Battery Electrode Materials Manufacturer
- Lithium-ion Battery Pack Supplier
- Lithium-ion Battery Powered Electronic Device Supplier
_______________________________________________________________________________
LiFePO4 battery packs
- Long Life: Olivine structured cathode capable to take strain during cycling better than the conventional LiCoO2 Cathode resulting in high cycle life
- High Power: High structural stability of the cathode offers high power discharge. Rated discharge capacity 0.5C to 10C
- Quick charge: Pack can be charged within 4-6 hours. Individual cells @1C
- High Energy: High Nominal capacity of 140-145 mAh/g
- Safe: Fe-chemistry is safe than that of Cobalt. No leakage, No fire, No smoke, thus environment friendly
- Temperature operation: Wide range of operation between -40°C to 65°C
________________________________________________________________________________
Lithium-Ion batteries: Design Flexibilities

_______________________________________________________________________________
Green Energy
Hi-Tech applications made possible by LIB’s




